Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Nomizu, Daiki*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Yuji
Hydrometallurgy, 199, p.105539_1 - 105539_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.99(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The synergistic solvent extraction of lanthanide(III) with mixtures of di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (D2EHPA, A) and monoisodecyl phosphoric acid (MIDPA, B) in phosphonium-based ionic liquid was investigated. In the case of D2EHPA or MIDPA single extractant system, Ln(III) (Ln = Pr and Nd) was extracted as [LnA HA] or [LnB
HA] or [LnB HB], respectively, the extracted species of Tb(III) or Dy(III) were determined by slope analysis. According to the equilibrium constants (
HB], respectively, the extracted species of Tb(III) or Dy(III) were determined by slope analysis. According to the equilibrium constants (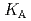 ,
, 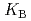 and
and 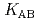 ) and the formation constants (
) and the formation constants (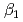 ,
, 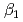 and
and 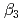 ), it was found that the extracted complex [TbHA
), it was found that the extracted complex [TbHA B
B or [DyHA
or [DyHA B
B ] was more stable than [LnA
] was more stable than [LnA HA] or [LnB
HA] or [LnB HB]. The synergistic extraction effects were investigated to study the possibility of separating Dy(III) from Pr(III) and Nd(III) according to their separation factors.
HB]. The synergistic extraction effects were investigated to study the possibility of separating Dy(III) from Pr(III) and Nd(III) according to their separation factors.
Kato, Chiaki
Comprehensive Nuclear Materials, 2nd Edition, Vol.4, p.528 - 563, 2020/08
In spent fuel reprocessing plants, various nitric media are encountered throughout the PUREX process, used in the separation of fission products, uranium, and plutonium. The PUREX process is thus highly corrosive as it takes place at high temperatures under high concentrations of nitric acid solution containing oxidizing metal ions from spent fuel. In this review, the unique chemical properties of nitric acid are first described. Secondly, the process of oxidizing power generation in boiling nitric acid under heat transfer is described using the redox potential and a thermodynamic model of boiling nitric acid. Finally, the corrosion behavior and corrosion acceleration mechanism specific to the reprocessing environments are described from the perspective of solution chemistry.
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Miyahara, Shinya; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.513 - 520, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study revealed melting points and thermal conductivities of four samples generated by sodium-concrete reaction (SCR). We prepared the samples using two methods such as firing mixtures of sodium and grinded concrete powder, and sampling depositions after the SCR experiments. In the former, the mixing ratios were determined from the past experiment. The latter simulated the more realistic conditions such as the temperature history and the distribution of Na and concrete. The thermogravimetry-differential thermal analyzer (TG-DTA) measurement showed the melting points were 865-942 C, but those of the samples containing metallic Na couldn't be clarified. In the two more realistic samples, the compression moldings in a furnace were observed. The observation revealed the softening temperature was 800-840
C, but those of the samples containing metallic Na couldn't be clarified. In the two more realistic samples, the compression moldings in a furnace were observed. The observation revealed the softening temperature was 800-840 C and the melting point was 840-850
C and the melting point was 840-850 C, which was 10-20
C, which was 10-20 C lower than the TG-DTA results. The thermodynamics calculation of FactSage 7.2 revealed the temperature of the onset of melting was caused by melting of the some components such as Na
C lower than the TG-DTA results. The thermodynamics calculation of FactSage 7.2 revealed the temperature of the onset of melting was caused by melting of the some components such as Na SiO
SiO and/or Na
and/or Na SiO
SiO . Moreover, the thermal conductivity was
. Moreover, the thermal conductivity was  =1-3W/m-K, which was comparable to xNa
=1-3W/m-K, which was comparable to xNa O-1-xSiO
O-1-xSiO (x=0.5, 0.33, 0.25), and those at 700
(x=0.5, 0.33, 0.25), and those at 700 C were explained by the equation of
C were explained by the equation of 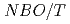 .
.
 setting approaches for rocks for the performance assessment of geological disposal; Application for granitic rocks
setting approaches for rocks for the performance assessment of geological disposal; Application for granitic rocksTachi, Yukio; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Shibutani, Sanae*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 24(2), p.109 - 133, 2017/12
For performance assessment (PA), the distribution coefficient (K ) need to be determined taking into account the specific PA conditions, including geochemical variability or uncertainty. The K
) need to be determined taking into account the specific PA conditions, including geochemical variability or uncertainty. The K setting approach for rocks was developed by integrating three methods; (i) direct use of measured K
setting approach for rocks was developed by integrating three methods; (i) direct use of measured K data extracted from the sorption database, (ii) semi-quantitative estimation by scaling differences between experimental and PA conditions, and (iii) thermodynamic sorption models. This approach was tested for granitic rock by comparing K
data extracted from the sorption database, (ii) semi-quantitative estimation by scaling differences between experimental and PA conditions, and (iii) thermodynamic sorption models. This approach was tested for granitic rock by comparing K values and their uncertainties of Cs and Am. The results indicated that K
values and their uncertainties of Cs and Am. The results indicated that K can be quantitatively evaluated by all approaches when adequate data and models are available. The K
can be quantitatively evaluated by all approaches when adequate data and models are available. The K dataset for safety-relevant 25 radionuclides was developed based on the direct use of measured data, and compared with the recent K
dataset for safety-relevant 25 radionuclides was developed based on the direct use of measured data, and compared with the recent K dataset in European PA projects. This K
dataset in European PA projects. This K setting approaches allowed to estimate the K
setting approaches allowed to estimate the K values and their uncertainties under the expected site conditions.
values and their uncertainties under the expected site conditions.
 by Knudsen effusion mass spectrometry
by Knudsen effusion mass spectrometryNakajima, Kunihisa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 491, p.183 - 189, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:61.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)One of the main chemical forms of cesium in the gas phase during severe accidents of light water reactor is expected to be cesium metaborate, CsBO , by thermodynamic equilibrium calculation considering reaction with boron. But accuracy of the thermodynamic data of gaseous metaborate, CsBO
, by thermodynamic equilibrium calculation considering reaction with boron. But accuracy of the thermodynamic data of gaseous metaborate, CsBO (g), has been judged as poor quality. Thus, Knudsen effusion mass spectrometric measurement of CsBO
(g), has been judged as poor quality. Thus, Knudsen effusion mass spectrometric measurement of CsBO was carried out to obtain reliable thermodynamic data. The evaluated values of standard enthalpy of formation of CsBO
was carried out to obtain reliable thermodynamic data. The evaluated values of standard enthalpy of formation of CsBO (g),
(g), 
 H
H
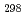 (CsBO
(CsBO ,g), by the 2nd and 3rd law treatments are -700.7
,g), by the 2nd and 3rd law treatments are -700.7 10.7 kJ/mol and -697.0
10.7 kJ/mol and -697.0 10.6 kJ/mol, respectively, and agree with each other within the errors, which suggests our data are reliable. Further, it was found that the existing data of the Gibbs energy function and the standard enthalpy of formation agreed well with the values evaluated in this study, which indicates the existing thermodynamic data are also reliable.
10.6 kJ/mol, respectively, and agree with each other within the errors, which suggests our data are reliable. Further, it was found that the existing data of the Gibbs energy function and the standard enthalpy of formation agreed well with the values evaluated in this study, which indicates the existing thermodynamic data are also reliable.
Kurata, Masaki; Shirasu, Noriko; Kawakami, Kazuto*
Proceedings of Annual Topical Meeting on Reactor Fuel Performance (TopFuel 2015) (Internet), p.139 - 156, 2015/09
Thermodynamic database is a useful tool for evaluating preliminary chemical reactions during molten core concrete interaction and phase relations in fuel debris. Japan Atomic Energy Agency and Nippon Steel Sumitomo Metal Corporation are collaborating to develop an open thermodynamic database by combining their own nuclear- and steel/slag-databases. The phase diagrams of Al O
O -UO
-UO , Al
, Al O
O -ZrO
-ZrO , SiO
, SiO -UO
-UO , and UO
, and UO -ZrO
-ZrO sub-systems and those of Al
sub-systems and those of Al O
O -UO
-UO , SiO
, SiO -UO
-UO , and Al
, and Al O
O -ZrO
-ZrO sub-systems were able to be drawn properly using the cell model parameters and the sub-lattice model parameters assessed in the present study, respectively. The concerns for improving accuracy on the assessment were extracted in several sub-systems.
sub-systems were able to be drawn properly using the cell model parameters and the sub-lattice model parameters assessed in the present study, respectively. The concerns for improving accuracy on the assessment were extracted in several sub-systems.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Minase, Naofumi; Iida, Yoshihisa; Tanaka, Tadao; Nakayama, Shinichi
JAERI-Conf 2005-007, p.150 - 155, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Arai, Yasuo
Kaku Nenryo, (40), p.40_21 - 40_25, 2005/01
no abstracts in English
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Minato, Kazuo
JAERI-Conf 2003-005, 186 Pages, 2003/06
Applications of molten salts technology to separation and synthesis of materials have been widely studied. Especially, much attention is given to the pyrochemical reprocessing of spent nuclear fuels. Computer simulation technique is expected to play an important role for supporting experimental works and predicting unknown physical properties in the molten salts application studies. Research group for Actinides Science, Department of Materials Science, Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), together with Reprocessing and Recycle Technology Division, Atomic Energy Society of Japan, organized the 2nd Workshop on Molten Salts Technology and Computer Simulation at Tokai Research Establishment, JAERI on December 3, 2002. Many molten salts researchers in Japan participated in the workshop and many useful presentations and discussions were performed.
Kato, Chiaki; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Corrosion Engineering, 52(1), p.69 - 85, 2003/01
It is necessary to know the generation mechanism of high equilibrium potential in the solutions. Existing nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions were first analyzed by Raman spectroscopy and then existing amount of nitrogen oxides were examined by thermodynamic calculation using the SOLGASMIX software. The Raman spectroscopic analysis showed that the existing amount of un-dissociated HNO increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO
increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO , NO
, NO
 , HNO
, HNO , NO
, NO , and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO
, and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO /HNO
/HNO equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
Kato, Chiaki; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 52(1), p.44 - 52, 2003/01
In order to understand corrosion of metals in nitric acid solutions, it is necessary to know the generation mechanism of high equilibrium potential in the solutions, especially under boiling conditions. The Raman spectroscopic analysis showed that the existing amount of un-dissociated HNO increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The existing amount of NO
increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The existing amount of NO also increased by thermal decomposition. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO
also increased by thermal decomposition. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO , NO
, NO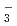 , HNO
, HNO , NO
, NO , and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO
, and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO /HNO
/HNO equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
 solid solution with magnesium and europium oxides
solid solution with magnesium and europium oxidesFujino, Takeo*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Yamada, Kota*; Nakama, Shohei*; Fukuda, Kosaku; Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Shiratori, Tetsuo*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 297(3), p.332 - 340, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.39(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Oxygen potential of solid solution Mg Eu
Eu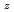 U
U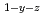 O
O was examined as a function of O/Metal ratio at 1000, 1100 and 1200
was examined as a function of O/Metal ratio at 1000, 1100 and 1200 C. The O/Metal ratio which gave the steepest change of the oxygen potential(GOM) was 1.995 for y=0.05, z=0.1 and y=0.05, z=0.05. The position decreased to 1.908 at higher Mg
C. The O/Metal ratio which gave the steepest change of the oxygen potential(GOM) was 1.995 for y=0.05, z=0.1 and y=0.05, z=0.05. The position decreased to 1.908 at higher Mg concentration of y=0.1, z=0.05. The GOM did not change with temperature in a range 1000-1200
concentration of y=0.1, z=0.05. The GOM did not change with temperature in a range 1000-1200 C. At GOM, a friction of 0.473 of total Mg
C. At GOM, a friction of 0.473 of total Mg occupy the interstitial position of the fluorite lattice.
occupy the interstitial position of the fluorite lattice.
Nitani, Noriko; Kuramoto, Kenichi; Yamashita, Toshiyuki; Omichi, Toshihiko*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 38(3-4), p.435 - 438, 2001/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji
JAERI-Data/Code 2000-031, 131 Pages, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
J. A. BERRY*; M. BROWNSWORD*; D. J. ILETT*; Linklater, C. M.*; Mason, C.*; TWEED, C. J.*
JNC TJ8400 2000-060, 60 Pages, 2000/02
Batch sorption experiments have been carried out to investigate the sorption behaviour of plutonium onto basalt and sandstone from the appropriate rock-equilibrated waters under different redox eonditions. Redox Potentials in solution were controlled by the addition of two reducing agents and one oxidising agent. Thermodynamic chemical modelling was undertaken to interpret the results. The sorption models were based on iron oxide. They adequately reproduced the data for sorption of plutonium onto sandstone, but tended to underpredict sorption onto basalt.
Sakamura, Y.*; Shirai, Osamu; Iwai, Takashi; Suzuki, Yasufumi
Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 147(2), p.642 - 649, 2000/02
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:61.09(Electrochemistry)no abstracts in English
Savage, D.*; Lemke, K.*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Shibata, Masahiro; Arthur, R. C,*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 2000-004, 30 Pages, 2000/01
Modeling approaches that have been proposed for cement-water system are reviewed in this report, and relevant supporting thsrmodynamic data are compiled. The thermodynamic data include standard molal thermodynamic properties of minerals and related compounds comprising cements, and equilibrium constants for associated hydrolysis reactions. Similar data for minerals that are stable in hyperalkaline geologic environments (e.g., zeolites) are also included because these minerals could be formed as hyperalkaline fluids emanating from cementitious matelials in a repository for radioactive wastes interact with the surrounding host rock. Standard molal properties (i.e., standard molal Gibbs free energies and enthalpies of formation and standard molal entropies), and/or equilibrium constants for associated hydrolysis reactions, are included for. (1)cement minerals and related compounds (Reardon, 1992; Glasser et al., 1999) (2)calcium-silicate hydrate minerals (Sarkar et al., 1982), and (3)zeolites (calorimetric and estimated values from various sources) All these data are accepted at face value, and it is therefore cautioned that the data, considered as a whole, may not be internally consistent. It is also important to note that the accuracy of these data have not been evaluated in the present study. Several models appropriate for cement-water systems have been proposed in recent years. Most are similar in the sense that they represent empirical fits to laboratory data for the CSH gel-water system, and therefore not thermodynamically defensible. An alternative modeling approach based on thermodynamic principles of solid-solution behavior appropriate for CSH gel has recently been proposed, however. It is reviewed in the present study, and evaluated in relation to experimental results obtained by JNC on cement-water interactions. The solid-solution model is based upon a thermodynamically- and structually-justifiable description of CSH gel in terms of a non-ideal ...
Ashida, Takashi; ; Sato, Haruo; ; Kitamura, Akira; Kawamura, Kazuhiro
JNC TN8400 99-083, 63 Pages, 1999/11
Studies on the chemical and migration behaviour of radionuclides were carried out in the Quantitative Assessment Radionuclide Migration Experimental Facility (QUALITY)for assuring the relaiability and for improving the propriety of data concerning nuclide migration used in the Second Progress Report for the geoloical disposal of high-level radioactive waste. Five studies for solubility, sorption and diffusion concerning nuclide migration were carried out. The overview of each study and the result is as follows: (1)Study on Effect of Carbonate on Np Solubility. Solubilities of Np(IV) were measured as functions of pH and carbonate concentration under reducing conditions. The obtained data could be well described by considering two hydroxo-carbonate complexes, and those stability constants were estimated and compared with the literature data. Consequently, the data obtained in this study were similar to the literature data. (2)Study on Effect of Carbonate on Np Sorption on Bentonite. Distribution coefficients (Kd) of Np(IV) on smectite were measured as a function of carbonate concentration. The obtained Kd values were approximately constant over the carbonate concentration (total carbon concentration 0.04-0.15M). The results of desorption tests by 1M KCl and HCl at the end of sorption experiments showed two different desorption behaviour; Np(IV) was well removed by HCl for the experiments in low carbonate concentration and by KCl for those in high carbonate concentration. (3)Distribution Coefficient Measurements for Cs, Pb and Cm on Rocks. Distribution Coefficients for Cs, Pb and Cm on Japanese major rocks (basalt, mudstone, sandstone, granodiorite and tuff) were measured as a function of ionic strength. The obtained Kd values were either the same orders or higher compared with data used to both fresh and saline groundwater systems in the Second Progress Report. This indicates that the Kd data used in the Second Progress Report are either proper or conservative. ...
Yui, Mikazu; ; Shibata, Masahiro
JNC TN8400 99-070, 106 Pages, 1999/11
This report is a summary of status, frozen datasets, and future tasks of the JNC thermodynamic database (JNC-TDB) for assessing performance of high-level radioactive waste in geological environments. The JNC-TDB development was carried out after the first progress report on geological disposal research in Japan (H3). In the development, thermodynamic data (equilibrium constants at 25  C, I=0) for important radioactive elements were selected/determined based on original experimental data using different models (e.g., SIT, Pitzer). As a result, the reliability and traceability of the data for most of the important elements were improved over those of the PNC-TDB used in H-3 report. For detailed information of data analysis and selections for each element, see the JNC technical reports listed in this document.
C, I=0) for important radioactive elements were selected/determined based on original experimental data using different models (e.g., SIT, Pitzer). As a result, the reliability and traceability of the data for most of the important elements were improved over those of the PNC-TDB used in H-3 report. For detailed information of data analysis and selections for each element, see the JNC technical reports listed in this document.
*; Sato, Haruo; *
JNC TN8400 99-059, 59 Pages, 1999/10
Organic acids in groundwater are considered to form complexes and increase the solubility of radionuclides released from vitrified waste in a high-level radioactive waste (HLW) repository. To ivestigate whether the solubility of samarium (Sm) is influenced by organic substances, we measured Sm solubility in the presence of different organic substances and compared those values with results from thermodynamic predictions. Humic acid (Aldrich) is commercially available and soluble organic matter originated from bentonite were used as organic substances in this study. Consequently, the solubility of Sm showed a tendency to apparently increase with icreasing the concentration of humic acid, but in the presence of carbonate, thermodynamic predictions suggested that the dominant species are carbonate complexes and that the effect of organic substances are less than that of carbonate. Based on total organic carbon (TOC), the increase of Sm solubility measured with humic acid (Aldrich) was more significant than that in the case with soluble organic matter originated from bentonite. Since bentonite is presumed to include also simple organic matters of which stability constant for forming complexes is low, the effect of soluble organic matter originated from bentonite on the solubility of Sm is eonsidered to be less effective than that of humic acid (Aldrieh). Experimental values were compared with model prediction, propsed by Kim, based on data measured in a low pH region. Tentatively we calculated the increase in Sm solubility assuming complexation with humic acid. Trial calculations were carried out on the premise that the complexation reaction of metal ion with humic acid is based on neutralization process by 1-1 complexation. In this process, it was assumed that one metal ion coordinates with one unit of complexation sites which number of proton exchange sites is equal to ionic charge. Consequently, Kim's model indicated that carbonate complexes should be dominant ...